Abstract
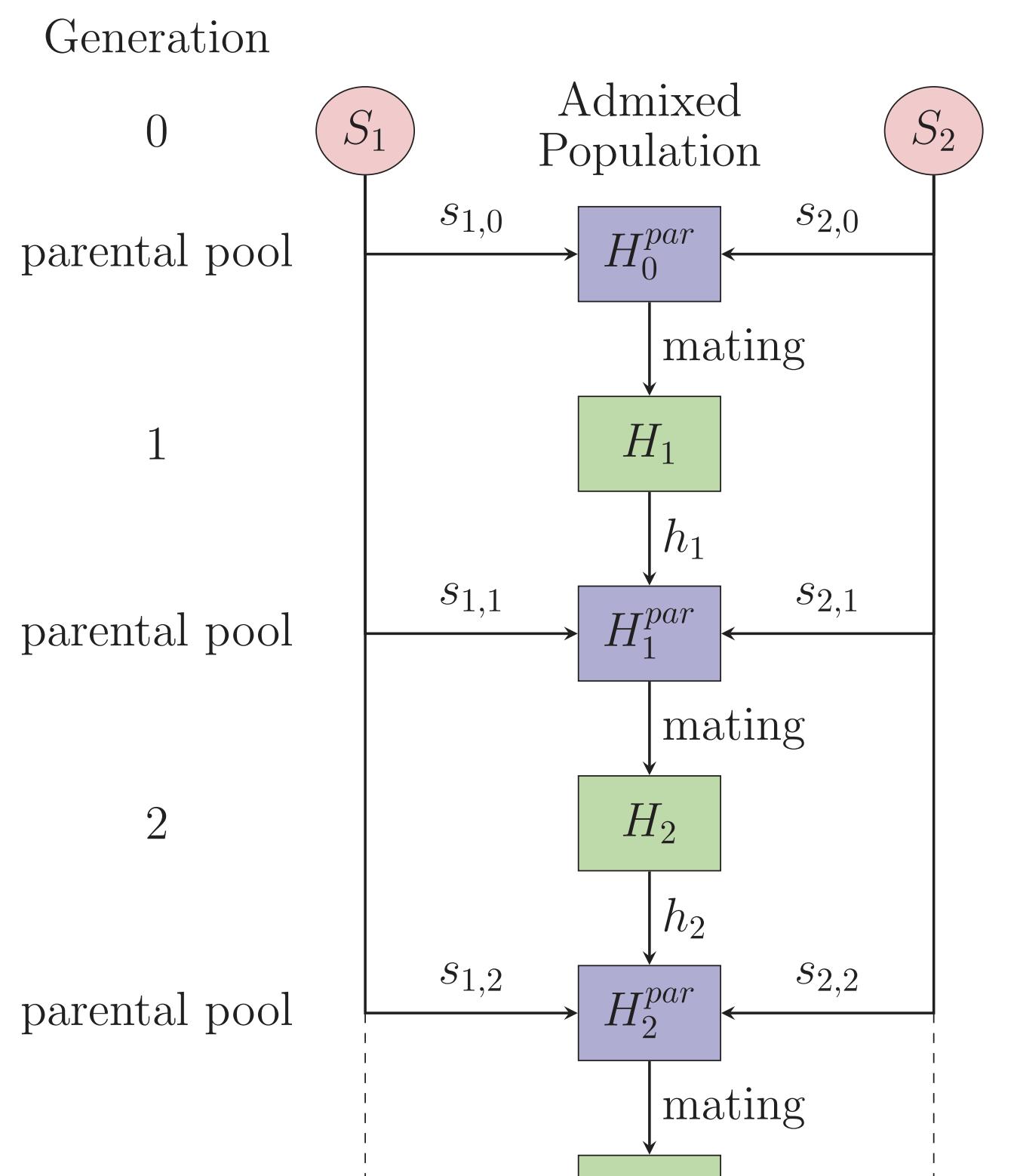
In genetic admixture processes, source groups for an admixed population possess distinct patterns of genotype and phenotype at the onset of admixture. Particularly in the context of recent and ongoing admixture, such differences are sometimes taken to serve as markers of ancestry for individuals—that is, phenotypes initially associated with the ancestral background in one source population are assumed to continue to reflect ancestry in that population. Such phenotypes might possess ongoing significance in social categorizations of individuals, owing in part to perceived continuing correlations with ancestry. However, genotypes or phenotypes initially associated with ancestry in one specific source population have been seen to decouple from overall admixture levels, so that they no longer serve as proxies for genetic ancestry. Here, we aim to develop an understanding of the joint dynamics of admixture levels and phenotype distributions in an admixed population.